A fellowship alumnus helps himself and others to research on Argonne’s Aurora supercomputer.
Argonne National Laboratory

New home for science and tech talk
With the fifth season’s first episode, a DOE CSGF-sponsored podcast launches a website.
Decisive achievement
A computational sciences fellow models COVID-19 virus variants and examines how people weigh complex decisions.
A colorful career
Argonne’s Joe Insley combines art and computer science to build intricate images and animations from supercomputer simulations.
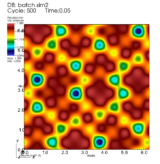
Mapping the metastable
An Argonne National Laboratory group uses supercomputers to model known and mysterious atomic arrangements, revealing useful properties.
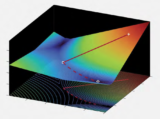
Optimized for discovery
A computational mathematician finds a national lab ideal for a highly collaborative career.

Extreme 3D
Argonne’s Advanced Photon Source upgrades to large-sample 3-D imaging beyond the depth of field – with assistance from high-performance computing.

Banishing blackouts
An Argonne researcher upgrades supercomputer optimization algorithms to boost reliability and resilience in U.S. power systems.
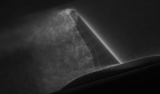
Beyond the tunnel
Stanford-led team turns to Argonne’s Mira to fine-tune a computational route around aircraft wind-tunnel testing.
Visions of exascale
Argonne National Laboratory’s Aurora will take scientific computing to the next level. Visualization and analysis capabilities must keep up.

Chipping away
Redirecting an old chip might change the pathway to tomorrow’s fastest supercomputers, Argonne National Laboratory researchers say.

Bright future
The smart grid turns to high-performance computing to guide its development and keep it working.
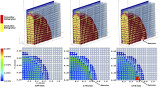
Sneak kaboom
At Argonne, research teams turn to supercomputing to study a phenomenon that can trigger surprisingly powerful explosions.
Rewinding the universe
Dark energy propels the universe to expand faster and faster. Researchers are using simulations to test different conceptions about how this happens.
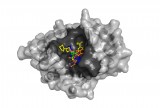
Overcoming resistance
To find a path around antibiotic resistance, a team working with the Intrepid supercomputer at Argonne National Laboratory is simulating molecular binding interactions to rapidly vet new infection-fighting candidates.
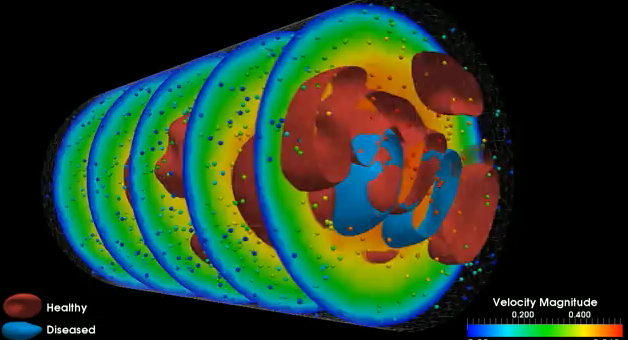
Inside the skull
Modeling the elements of blood flow in the brain could help neurosurgeons to predict when and where an aneurysm might rupture – and when to operate.
Pounding out atomic nuclei
Thousands of tiny systems called atomic nuclei – specific combinations of protons and neutrons – prove extremely difficult to study but have big implications for nuclear stockpile stewardship. To describe all of the nuclei and the reactions between them, a nationwide collaboration is devising powerful algorithms that run on high-performance computers.
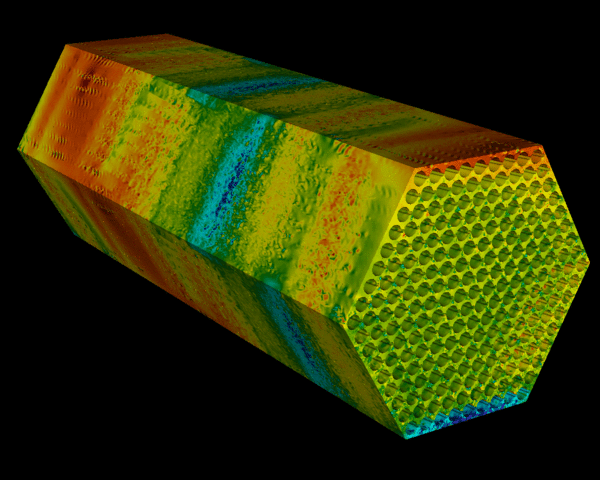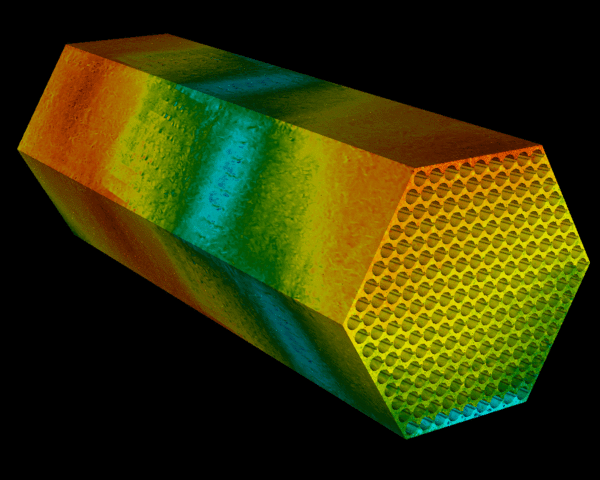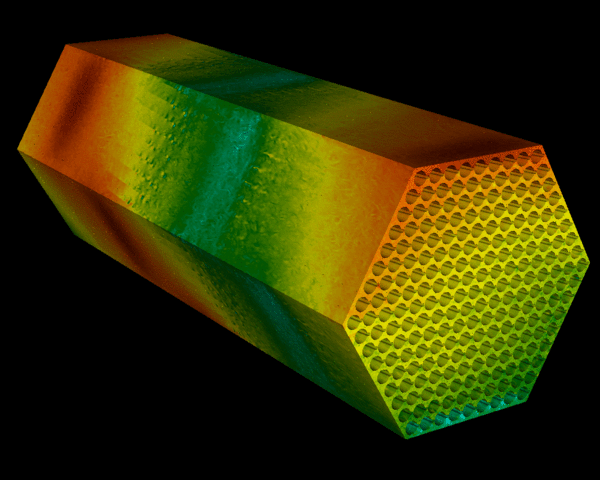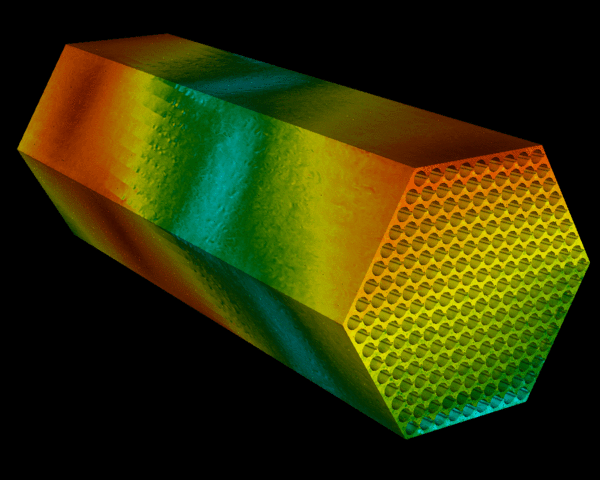
Nuclear predictive
Argonne National Laboratory applies mathematics and computation to engineer the next generation of nuclear reactors.
Putting catalysts on track
Computation and experimentation combine to improve and speed design of useful compounds.